How Does the Electron-cloud Model Describe Electrons
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1008 hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. The free electron model can be used to.

Electron Configurations Describe Where Electrons Are Located Around The Nucleus Of An Atom For Example The Electron Configuration Electrons Atomic Structure
Thomsons plum pudding model of the atom was incorrect.

. This means that the electron cloud for iodide can begin partial bond. This atomic model is known as the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Nucleophilicity Is Measured By Reaction Rate.
Its monatomic form H is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe constituting. In the space provided write the letter of the term or phrase that. The Lewis model allows us to describe exactly the same set of reactions as does the BrønstedLowry model.
When a species is donating a pair of electrons to a hydrogen more specifically a proton H we call it a base. Because outer electrons of metal atoms are delocalized and highly mobile metals have electrical and thermal conductivity. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1008 hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table.
Metallic bonds electrostatic interactions between the ions and the electron cloud hold the metallic solid together. Delocalized electrons surround the ions. Atoms are arranged like closely packed spheres.
This post attempts to address one of the most. Atoms are arranged like closely packed spheres. It was developed in 1927 principally by Arnold Sommerfeld who combined the classical Drude model with quantum mechanical FermiDirac statistics and hence it is also known as the DrudeSommerfeld model.
In this module students reconnect with and deepen their understanding of statistics and probability concepts first introduced in Grades 6 7 and 8. This electron transfer model is extended to liquidsolid interfaces leading to a revision of the formation mechanism of the electric double layer at liquidsolid interfaces. Rutherfords new model for the atom based on the experimental results contained.
Algebra I Module 2. A very large anion-like iodide has a very polarizable electron cloud because the electrons extend much further out from the nucleus than for example the electron cloud in fluoride. This meant that atoms could be divided into smaller parts.
Delocalized electrons surround the ions. Given its simplicity it is surprisingly. The Rutherford model was devised by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford to describe an atomRutherford directed the GeigerMarsden experiment in 1909 which suggested upon Rutherfords 1911 analysis that J.
An electron-cloud overlap model is proposed to explain CE in general. The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. This model can be portrayed as a nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structureThe chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. Second by adding a time-dependent polarization term P s created by the CE-induced surface electrostatic charges in the. Unlike the Bohr model the quantum mechanical model does not define the exact path of an electron but rather predicts the odds of the location of the electron.
Metallic bonds electrostatic interactions between the ions and the electron cloud hold the metallic solid together. Because outer electrons of metal atoms are delocalized and highly mobile metals have electrical and thermal conductivity. When discussing nucleophilicity were specifically talking about donating a pair of electrons to an atom other than hydrogen usually carbon.
Where the cloud is most dense the. Its monatomic form H is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe constituting. Also credited with plum pudding model where electrons were like plums embedded in a positively charged pudding.
In solid-state physics the free electron model is a quantum mechanical model for the behaviour of charge carriers in a metallic solid. Responsible for discovering electron using cathode-ray experiment. Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.
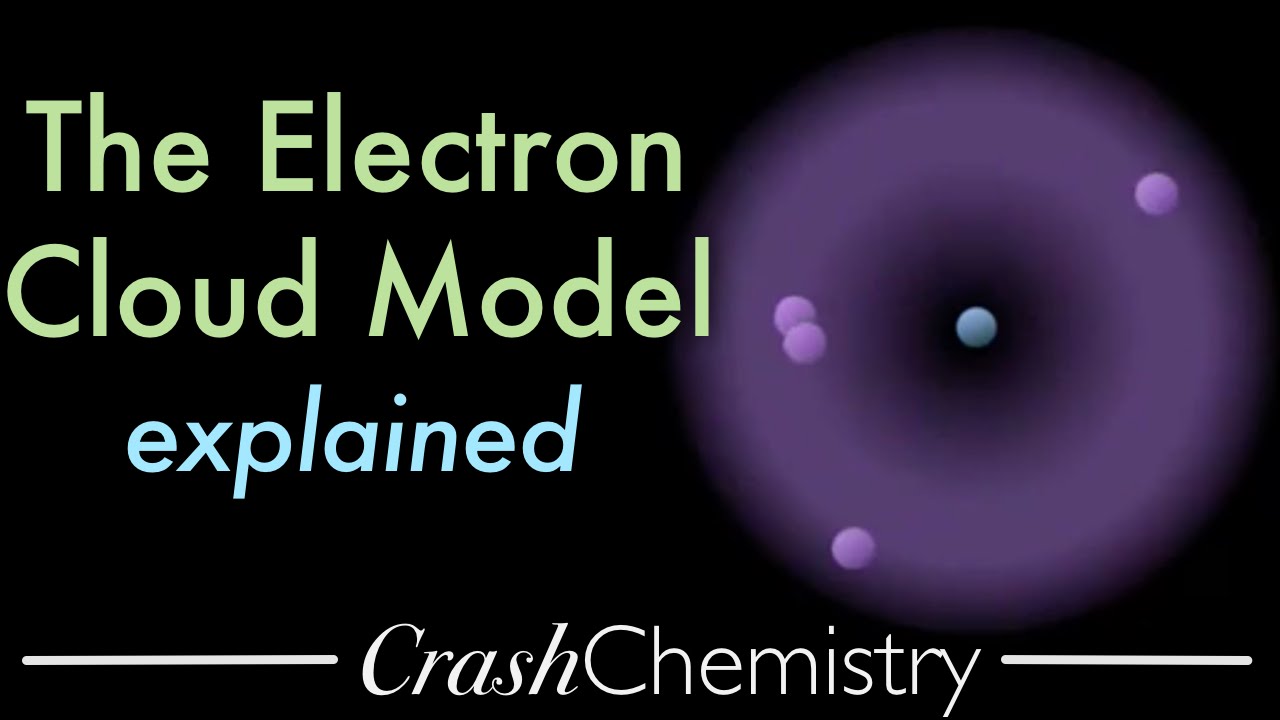
The Electron Cloud Model Explained Animation Atomic Orbitals Tutoria Lessons 2 And 3 Electrons Quantum Mechanics Chemistry

Atomic Structure Vocabulary Card Sort By The J Lab Tpt In 2021 Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons

Pin On Atomic Structure Protons Neutrons And Electrons

Atoms Lesson Plan A Complete Science Lesson Using The 5e Method Of Instruction Kesler Science Science Lessons Science Lesson Plans Kesler Science
0 Response to "How Does the Electron-cloud Model Describe Electrons"
Post a Comment